arXiv “Self-supervised Subgraph NN with Deep Reinforcement Walk Exploration”
arXiv paper of “Self-supervised Subgraph Neural Network With Deep Reinforcement Walk Exploration”
Our new paper has been submitted to arXiv.
-
Anchor Space Optimal Transport: Accelerating Batch Processing of Multiple OT Problems
- Author: Jianming Huang (D3), and HK
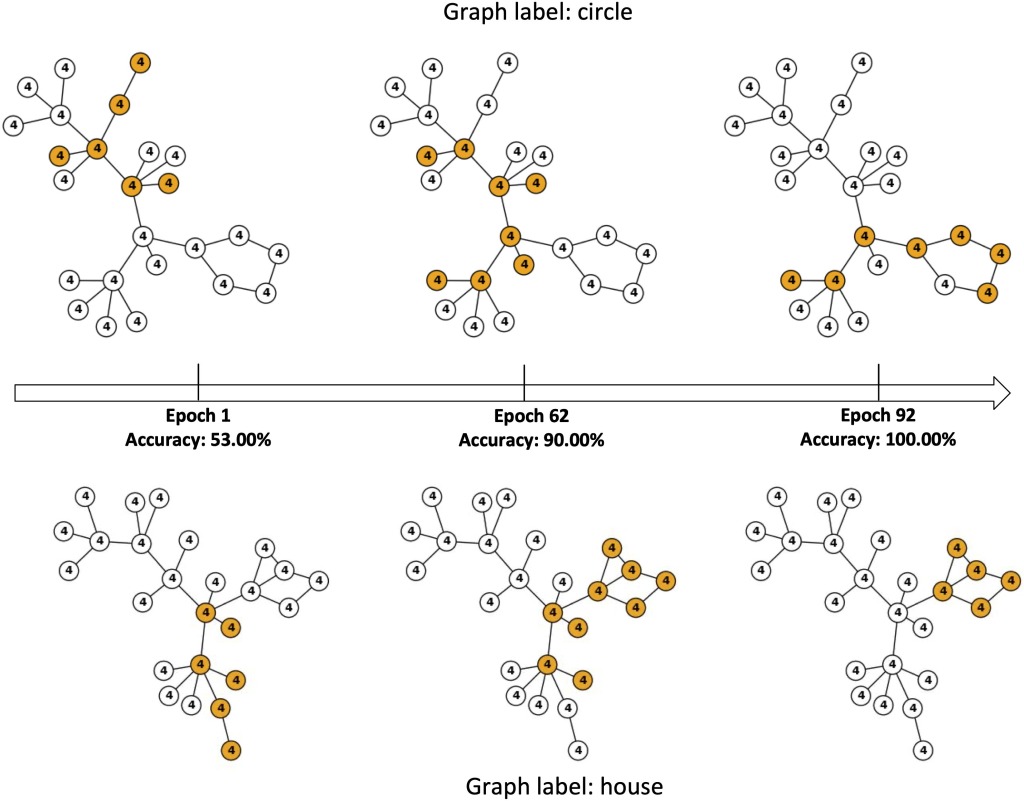
- Abstract: Graph data, with its structurally variable nature, represents complex real-world phenomena like chemical compounds, protein structures, and social networks. Traditional Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) primarily utilize the message-passing mechanism, but their expressive power is limited and their prediction lacks explainability. To address these limitations, researchers have focused on graph substructures. Subgraph neural networks (SGNNs) and GNN explainers have emerged as potential solutions, but each has its limitations. SGNNs compute graph representations based on the bags of subgraphs to enhance the expressive power. However, they often rely on predefined algorithm-based sampling strategies, which is inefficient. GNN explainers adopt data-driven approaches to generate important subgraphs to provide explanations. Nevertheless, their explanation is difficult to be translated into practical improvements on GNNs. To overcome these issues, we propose a novel self-supervised framework that integrates SGNNs with the generation approach of GNN explainers, named the Reinforcement Walk Exploration SGNN (RWE-SGNN). Our approach features a sampling model trained in an explainer fashion, optimizing subgraphs to enhance model performance. To achieve a data-driven sampling approach, unlike traditional subgraph generation approaches, we propose a novel walk exploration process, which efficiently extracts important substructures, simplifying the embedding process and avoiding isomorphism problems. Moreover, we prove that our proposed walk exploration process has equivalent generation capability to the traditional subgraph generation process. Experimental results on various graph datasets validate the effectiveness of our proposed method, demonstrating significant improvements in performance and precision.
- Paper: arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.01809
- Source code: Will be available soon.